Let’s now create a Simple Calculator App using Android Studio and Java. This app will allow users to perform basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division).
Step-by-Step Instructions:
1. Set Up Your Android Project
- Open Android Studio.
- Select New Project.
- Choose Empty Activity and click Next.
- Name your project CalculatorApp.
- Select Java as the programming language.
- Click Finish to create the project.
2. Design the Layout (XML)
We will design a simple calculator layout with number buttons (0-9), operator buttons (+, −, ×, ÷), a clear button, and an equal button.
activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/display1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="16dp"
android:focusable="true"
android:focusableInTouchMode="true"
android:textSize="32sp"
android:gravity="end"
android:hint="Num 1"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/display2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/display1"
android:layout_margin="16dp"
android:focusable="true"
android:focusableInTouchMode="true"
android:textSize="32sp"
android:gravity="end"
android:hint="Num 2"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/result_display"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/display2"
android:layout_margin="16dp"
android:textSize="32sp"
android:gravity="end"
android:text=""/>
<GridLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/result_display"
android:padding="16dp"
android:rowCount="5"
android:columnCount="4">
<Button android:id="@+id/button_1" android:text="1" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_2" android:text="2" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_3" android:text="3" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_4" android:text="4" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_5" android:text="5" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_6" android:text="6" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_7" android:text="7" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_8" android:text="8" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_9" android:text="9" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_0" android:text="0" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_dot" android:text="." style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_clear" android:text="C" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_plus" android:text="+" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_minus" android:text="-" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_multiply" android:text="×" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/button_divide" android:text="÷" style="@style/ButtonStyle"/>
</GridLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
This layout contains:
- A TextView to display the calculation result.
- Buttons for numbers, operators (
+,-,×,÷), and clear.
Add styles
styles.xml
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?>
<resources>
<style name=”ButtonStyle”>
</style>
</resources>
You can customize if you want.
3. Implement the Calculator Logic in Java
Now we’ll handle the button clicks and implement the calculation logic.
MainActivity.java
package com.example.simplecalculator;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.text.InputFilter;
import android.text.Spanned;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private EditText display1, display2;
private TextView resultDisplay;
private String operator;
private double valueOne, valueTwo;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
display1 = findViewById(R.id.display1);
display2 = findViewById(R.id.display2);
resultDisplay = findViewById(R.id.result_display);
// Set filters to allow only numbers and one dot
setInputFilter(display1);
setInputFilter(display2);
// Number buttons
setNumberButton(R.id.button_0, "0");
setNumberButton(R.id.button_1, "1");
setNumberButton(R.id.button_2, "2");
setNumberButton(R.id.button_3, "3");
setNumberButton(R.id.button_4, "4");
setNumberButton(R.id.button_5, "5");
setNumberButton(R.id.button_6, "6");
setNumberButton(R.id.button_7, "7");
setNumberButton(R.id.button_8, "8");
setNumberButton(R.id.button_9, "9");
setNumberButton(R.id.button_dot, "."); // Added dot button
// Operator buttons
findViewById(R.id.button_plus).setOnClickListener(v -> setOperator("+"));
findViewById(R.id.button_minus).setOnClickListener(v -> setOperator("-"));
findViewById(R.id.button_multiply).setOnClickListener(v -> setOperator("×"));
findViewById(R.id.button_divide).setOnClickListener(v -> setOperator("÷"));
// Clear button
findViewById(R.id.button_clear).setOnClickListener(v -> clear());
}
private void setInputFilter(EditText editText) {
editText.setFilters(new InputFilter[]{new DecimalInputFilter()});
}
private class DecimalInputFilter implements InputFilter {
@Override
public CharSequence filter(CharSequence source, int start, int end,
Spanned dest, int dstart, int dend) {
// If the input is empty, allow it
if (source.length() == 0) {
return null;
}
String input = dest.toString().substring(0, dstart) + source.toString() + dest.toString().substring(dend);
// Regex to check for valid decimal number
if (input.matches("^[0-9]*(\\.[0-9]+)?$")) {
return null; // Accept the input
}
return ""; // Reject the input
}
}
private void setNumberButton(int buttonId, String number) {
findViewById(buttonId).setOnClickListener(v -> {
// Determine which EditText is currently focused and append the number
if (display1.hasFocus()) {
// Allow only one dot in the first input
if (!display1.getText().toString().contains(".") || !number.equals(".")) {
display1.append(number);
}
} else {
// Allow only one dot in the second input
if (!display2.getText().toString().contains(".") || !number.equals(".")) {
display2.append(number);
}
}
});
}
private void setOperator(String op) {
if (!display1.getText().toString().isEmpty()) {
valueOne = Double.parseDouble(display1.getText().toString());
operator = op;
// Calculate immediately after setting the operator
if (!display2.getText().toString().isEmpty()) {
valueTwo = Double.parseDouble(display2.getText().toString());
calculate(); // Perform the calculation
}
display2.requestFocus(); // Set focus to the second display for the next number
}
}
private void calculate() {
if (!display2.getText().toString().isEmpty() && operator != null) {
valueTwo = Double.parseDouble(display2.getText().toString());
double result = 0;
switch (operator) {
case "+":
result = valueOne + valueTwo;
break;
case "-":
result = valueOne - valueTwo;
break;
case "×":
result = valueOne * valueTwo;
break;
case "÷":
if (valueTwo != 0) {
result = valueOne / valueTwo;
} else {
resultDisplay.setText("Error");
return;
}
break;
}
resultDisplay.setText(String.valueOf(result)); // Update result display
clearInputs(); // Clear inputs for next calculation
}
}
private void clearInputs() {
display1.setText(""); // Clear first input
display2.setText(""); // Clear second input
operator = null; // Reset operator
}
private void clear() {
clearInputs(); // Reset everything
resultDisplay.setText(""); // Clear result display
valueOne = 0;
valueTwo = 0;
}
}
4. Run the App
- Connect an Android device or use an emulator.
- Click the Run button in Android Studio.
- The app will launch, allowing you to:
- Enter numbers via the number buttons.
- Perform arithmetic operations via the operator buttons (
+,−,×,÷). - Use the C button to clear the input.
Output:
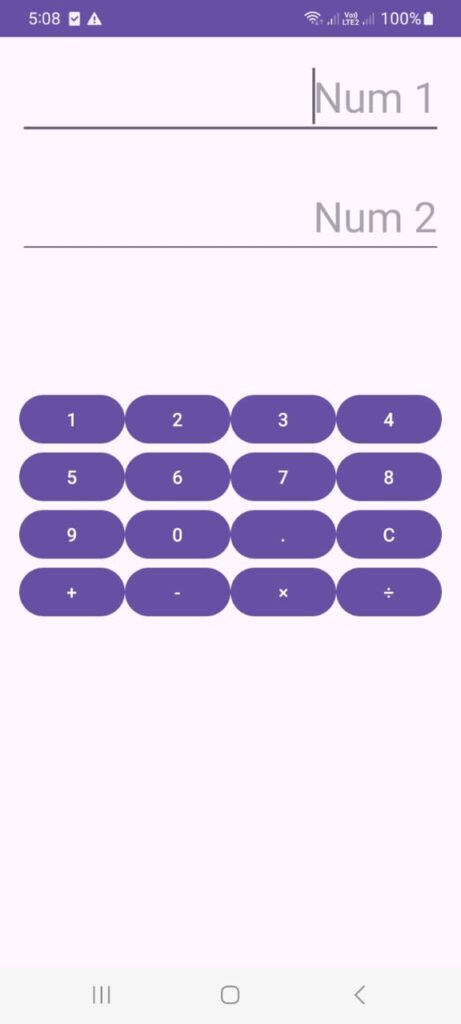
Key Points of the App:
- TextView displays the current number or result.
- Buttons for numbers (0-9), operators, and clear.
- Arithmetic operations are handled in Java using a simple switch-case structure.
- Clear resets the calculator to its initial state.
This project is a great way to learn how to handle user input, manage basic UI elements, and perform simple logic in an Android app.